Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
No Question or Answer Found.
You can search again using different keywords or check the previously asked question below manually.
You can search again using different keywords or check the previously asked question below manually.
question_answerWhat is ConVarT?
The conserved clinical variation visualization tool (ConVarT) is an online visualization resource developed by the Kaplan Lab, with the goal of displaying the evolutionary conservation of amino acid substitutions associated with diseases and non-clinically significant amino acid substitutions from ClinVar, COSMIC and gnomAD databases, and allowing easy access to collections of conserved genes and conserved variants associated with human diseases for the model organism research community. In addition, PTMs (post-translational modifications) are also integrated into the corresponding positions of amino acids on the human protein sequences.
question_answerWhat does ConVarT stand for?
The Conserved clinical Variation visualization Tool
question_answerHow may I use ConVarT?
Visualizing the presence of human genetic variants in the corresponding positions of the protein-encoding regions in other organisms currently remains to be difficult to handle with the available databases. ConVarT has integrated systematically human genetic variants from ClinVar, gnomAD and COSMIC into the corresponding positions of the protein-encoding regions in other organisms including Chimps, Macaca, Mice, Rat, Zebrafish, Xenopus, Drosophila, and C. elegans. In addition, PTMs (post-translational modifications) are also incorporated into the protein sequences and protein domains were generated from Pfam and joined with multiple sequence alignments.
On ConVarT, there are two different methods to make a search. Firstly, gene identifiers such as gene name, synonyms or species-specific gene-identifiers like MGI ID, FlyBase ID, etc. or "rs" number can be used simply in the search box on ConVarT. The detailed list of identifiers that can be used as an input in the search box is listed below table.
Secondly, we have developed a novel and innovative way to integrate unknown protein sequences into the ConVarT. Simply, any protein sequences without knowing gene identifiers can be copied and pasted into the search box on the ConVarT. This will use the protein blast (BLASTp) find the closest corresponding human protein sequence with the alignment of these two sequences, followed by the integration of relevant human genetic variants and PTMs. Protein domains from Pfam will be displayed together with human genetic variants and PTMs.

On ConVarT, there are two different methods to make a search. Firstly, gene identifiers such as gene name, synonyms or species-specific gene-identifiers like MGI ID, FlyBase ID, etc. or "rs" number can be used simply in the search box on ConVarT. The detailed list of identifiers that can be used as an input in the search box is listed below table.
| Identifier Name | Description |
|---|---|
| NCBI Gene ID | NCBI Gene ID (e.g. 6301) |
| Gene Symbol | Current Gene Symbol (e.g. SARS, sars-1) |
| Gene Synonmys | Previous Gene Symbols (e.g. SERRS) |
| HGNC | HUGO Gene Nomenclature Committee (e.g. HGNC:10537) |
| ENSEMBL GENE ID | ENSEMBL Gene IDs for any specie in our database (e.g. ENSG00000031698, ENSMUSG00000068739, ENSRNOG00000020255, ENSDARG00000008237, ENSPTRG00000001043, ENSMMUG00000021837) |
| RS Number | Reference SNP ID (e.g. rs1553178049) |
| Protein Acc. Number | NCBI Protein Accession Numbers (e.g. NP_006504.2, XP_006233198.1) |
| MGI ID | MGI-Mouse Genome Informatics (e.g. MGI:102809) |
| ZFIN ID | ZFIN The Zebrafish Information Network (e.g. ZDB-GENE-040831-1) |
| FB Gene ID | FlyBase Gene ID (e.g. FBgn0031497) |
| WB Gene ID | WormBase Gene ID(e.g. WBGene00005663) |
Secondly, we have developed a novel and innovative way to integrate unknown protein sequences into the ConVarT. Simply, any protein sequences without knowing gene identifiers can be copied and pasted into the search box on the ConVarT. This will use the protein blast (BLASTp) find the closest corresponding human protein sequence with the alignment of these two sequences, followed by the integration of relevant human genetic variants and PTMs. Protein domains from Pfam will be displayed together with human genetic variants and PTMs.

question_answerWhich model organisms are included in the database?
Human, chimp, macaca, zebrafish, mouse, rat, Xenopus, Drosophila and C. elegans.
However, with the new search feature, it is no longer limited to these model systems and any protein sequence from model systems can be searched with the visualization of human genetic variants and PTMs.
However, with the new search feature, it is no longer limited to these model systems and any protein sequence from model systems can be searched with the visualization of human genetic variants and PTMs.
question_answerWhich protein database is used in protein sequences to identify domains?
ConVarT has used the Pfam protein family database to automatically generate from human sequence data with a threshold of 1e-01 and they are then systematically integrated into the corresponding regions. Protein domains for human are illustrated in the multiple sequence alignments. In addition, the Pfam protein domain page can be accessed by clicking the domain illustration over the sequence or the links listed in the domain table.
question_answerIs it possible to retrieve the protein sequence used in multiple sequence alignments?
Yes, multiple sequence alignment section has a fixed species names on the left side. Clicking on the name of each species will direct you to the sequence and protein ID used.
question_answerHow the disease-associated genes data was generated?
The disease-associated genes were obtained from DisGeNET database.
question_answerWhat is the 'Conservation Scores' ?
Protein sequences of a gene have undergone constant evolutionary changes, although certain amino acids at critical positions have been preserved throughout evolution. For example, while most protein sequences encoded by histone genes are highly preserved throughout evolution, protein sequences of some proteins have undergone dramatic changes. A number of the amino acid substitutions may alter the protein functions (decrease or increase in function of proteins) and can not be tolerated due to the functional significance of these residues, thus leading a range of genetic diseases. Sequence alignment is one of the key bioinformatics techniques for revealing evolutionary relationships between the sequences. With the sequence alignment, the percentage of identical and similar amino acids can be identified.
Here, ConVarT has provided two different score types namely identity score and identity score for variation associated amino acids. Firstly, the identity score represents the percentage of identical amino acids of a gene in a species as compared to the human protein sequence. The protein sequences of each human gene were aligned with protein sequences of ortholog genes from other species using ClustalW sequence alignment algorithm. Afterward, the identity score for each protein transcript is determined by dividing the total number of identically matching aligned amino acids into the total number of amino acids. Secondly, the identity score for variation associated amino acids is calculated by the same approach. Simply, the number of amino acids with variation(s) was used instead of the number of all amino acids per number of all amino acids with variation(s).
Here is the interactive bar chart of conservation scores per gene on the gene page in ConVarT: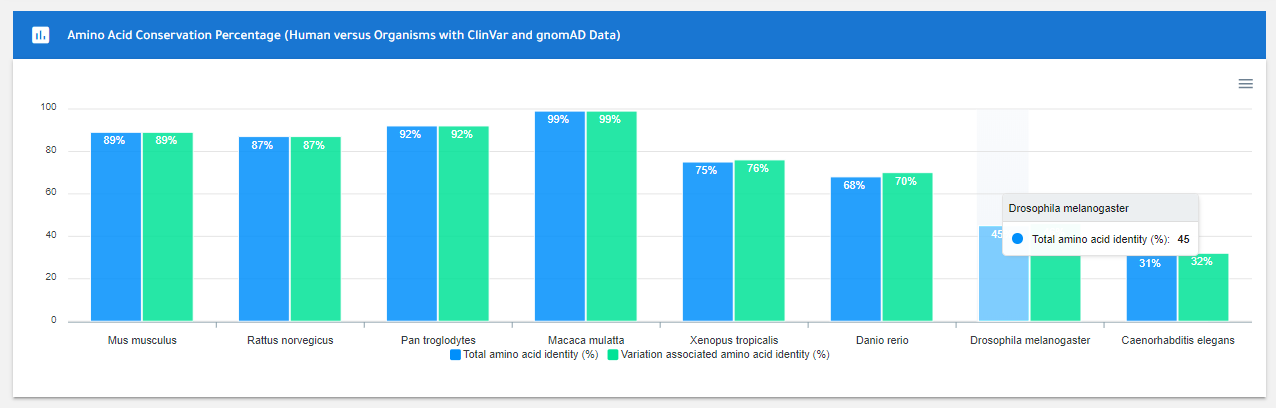
Here, ConVarT has provided two different score types namely identity score and identity score for variation associated amino acids. Firstly, the identity score represents the percentage of identical amino acids of a gene in a species as compared to the human protein sequence. The protein sequences of each human gene were aligned with protein sequences of ortholog genes from other species using ClustalW sequence alignment algorithm. Afterward, the identity score for each protein transcript is determined by dividing the total number of identically matching aligned amino acids into the total number of amino acids. Secondly, the identity score for variation associated amino acids is calculated by the same approach. Simply, the number of amino acids with variation(s) was used instead of the number of all amino acids per number of all amino acids with variation(s).
Here is the interactive bar chart of conservation scores per gene on the gene page in ConVarT:

question_answerHow to obtain all the orthologous genes between human and other species?
We compiled Chimp, Macaca, Mouse, Rat, and Xenopus orthologous proteins from
MGI Homology List. When we noticed that many Chimp and Macaca genes do not have human counterparts, we performed BLASTp analysis for the remaining genes. DIOPT (DRSC Integrative Ortholog Prediction Tool) was used to find human orthologs in Drosophila while human orthologs for C. elegans were generated with an in-house BLASTp pipeline together with the integration of literature search. For Zebrafish and human orthology matching, https://zfin.org/downloads/human_orthos.txt database was used. All the resulting the orthology gene list was compiled to achieve high accuracy in orthology, which is essentially needed for comparative analyses.
question_answerCan we access ConVarT via mobile phones or tablets?
Yes, they can be used but a laptop or desktop will provide a better visualization and access to data.
question_answer Can we make search with our own protein sequence to visualize the human genetic variants?
Yes, ConVarT enables researchers to search any protein sequence from any species and rapidly combines search with the integration of human genetic variants. For example, S. cerevisiae is not currently represented in the ConVarT. However, when the protein sequence of S. cerevisiae MLH1, the human homolog of MLH1, is copied and pasted on the ConVarT, ConVarT will discover human homolog of the protein sequence you've searched for and then enable you to view the pairwise sequence alignment of human homolog and the protein sequence you searched with integration of human genetic variants and PTMs.
question_answerI am facing a problem on the result page. What can I do?
We would be happy if you can fill "Feedback Form" via the feedback button on the right bottom corner of the result page.
question_answerHow often do you update the data sets used in ConVarT?
We are currently in the process of automating the update of the data sets from ClinVar, gnomAD, COSMIC and PTMs.
question_answerWhat if my variation does not appear in ConVarT?
It probably implies that the variant you have searched for may not be in protein-encoding regions, and ConVarT displays only the variations on the protein-encoding sequences. However, if your variant is in the protein encoding region and does not appear in ConVarT, please do not hesitate to contact us through our Contact page.
question_answerWill there be a development process in ConVarT ?
Yes, we are currently integrating additional resources that are publicly available and please feel free to contact us if you have any suggestions. For collaboration, please reach us out at
oktay.kaplan (at)agu.edu.tr .